자료구조
그래프(Graph)의 종류, 용어, 구현
CokeWorld
2021. 3. 19. 11:25
그래프란?
- 연결된 원소간의 관계를 표현하는 자료구조
- SNS 친구관계, 수도 배수 시스템, 물질의 분자구조 등에 적합한 자료구조
그래프의 종류
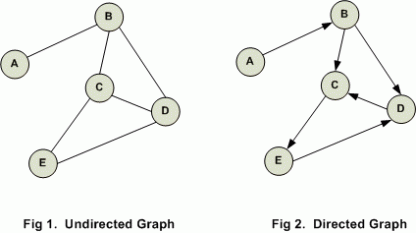
- 무방향 그래프(Undirected Graph)
- 두 정점을 연결하는 간선에 방향이 없는 그래프
- 방향 그래프(Directed Graph)
- 간선에 방향이 있는 그래프
- 완전 그래프(Complete Graph)
- 한 정점에서 다른 모든 정점과 연결 된 그래프
- 최대의 간선 수를 가진 그래프

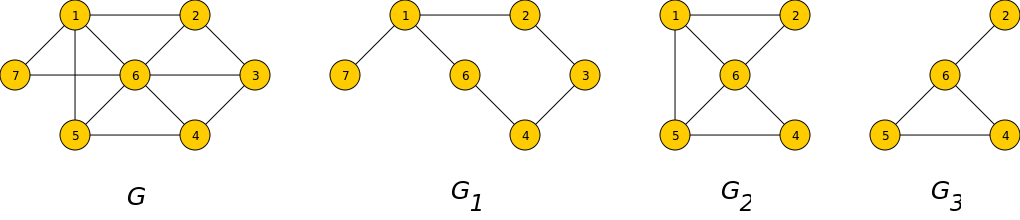
- 부분 그래프
- 원래의 그래프에서 일부의 정점이나 간선을 제외한 그래프
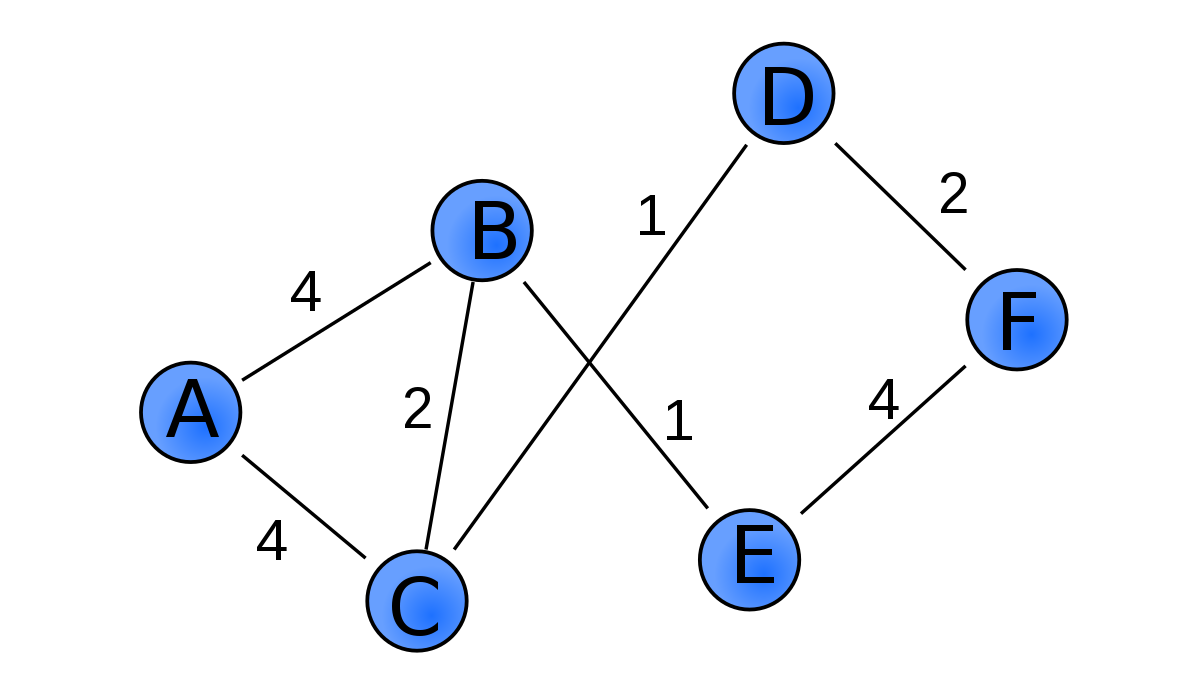
- 가중 그래프(Weight Graph)
- 간선에 가중치를 할당한 그래프
그래프 관련 용어
- 인접(adjacent): 그래프의 두 정점이 연결되어 간선이 있을 때, 두 정점을 인접되어 있다고 함.
- 부속(incident): 두 정점이 인접되어 있을 때, 간선은 두 정점에 부속되어 있다고 함.
- 차수(degree): 정점에 부속되어 있는 간선의 수
- 경로(path): 간선을 따라갈 수 있는 길
- 경로 길이(path length): 경로를 구성하는 간선의 수
- 단순 경로(simple path): 모두 다른 정점으로 구성된 경로
- 사이클(cycle): 단순 경로 중에서 경로의 시작 정점과 마지막 정점이 같은 경로
- DAG(Directed Acyclic Graph): 방향 그래프이면서 사이클이 없는 그래프
순차 자료구조 방식으로 그래프 구현: 인접 행렬
public class AdjacentMatrix {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AdjMatrix am = new AdjMatrix();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
am.insertVertex(i);
}
am.insertEdge(0,2);
am.insertEdge(0,4);
am.insertEdge(0,1);
am.insertEdge(1,2);
am.insertEdge(1,4);
am.insertEdge(2,4);
am.insertEdge(3,2);
am.insertEdge(3,1);
am.insertEdge(4,0);
am.insertEdge(4,1);
am.printAdjMatrix();
}
}
class AdjMatrix {
int matrix[][] = new int[10][10];
int totalVertex = 0;
public void insertVertex(int vertex) {
totalVertex++;
}
public void insertEdge(int vertex1, int vertex2) {
if (vertex1 >= totalVertex || vertex2 >= totalVertex) {
System.out.println("There is no vertex");
} else {
matrix[vertex1][vertex2] = 1;
}
}
public void printAdjMatrix() {
for (int i = 0; i < totalVertex; i++) {
System.out.printf("\n\t\t");
for (int j = 0; j < totalVertex; j++) {
System.out.printf("%2d", matrix[i][j]);
}
}
}
}연결 자료구조 방식으로 그래프 구현: 인접 리스트
public class AdjacentList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AdjList al = new AdjList();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
al.insertVertex(i);
}
al.insertEdge(0, 3);
al.insertEdge(0, 2);
al.insertEdge(0, 1);
al.insertEdge(1, 3);
al.insertEdge(1, 0);
al.insertEdge(2, 1);
al.insertEdge(2, 0);
al.insertEdge(3, 1);
al.insertEdge(3, 1);
al.insertEdge(4, 3);
al.printAdjList();
}
}
class GraphNode {
int vertex;
GraphNode link;
}
class AdjList {
private GraphNode head[] = new GraphNode[10];
private int totalVertex = 0;
// vertex 값을 입력하지 않는다.
// vertex 갯수 카운트용 메소드
public void insertVertex(int vertex) {
totalVertex++;
}
// vertex2 값을 내림차순으로 입력해야 함.
public void insertEdge(int vertex1, int vertex2) {
if (vertex1 >= totalVertex || vertex2 >= totalVertex) {
System.out.println("Vertex is out of range");
} else {
GraphNode gNode = new GraphNode();
gNode.vertex = vertex2;
gNode.link = head[vertex1];
head[vertex1] = gNode;
}
}
public void printAdjList() {
for (int i = 0; i <= totalVertex; i++) {
System.out.printf("\n정점 "+ i +"의 인접리스트 ");
GraphNode gNode = head[i];
while (gNode != null) {
System.out.printf("-> " + gNode.vertex);
gNode = gNode.link;
}
}
}
}
학습 교재